Feudalism Definition For Kids
Glossary and TermsApprentice - A boy who worked for a guild master in order to learn a trade or craft.Baron - A ruler below the king in the feudal system, the baron ruled an area of land called a fief. He would pledge his loyalty to the king in return for the land.Bishop - A leader in the church, the bishop was often the top church leader in a kingdom.Byzantine Empire - The eastern half of the Roman Empire that was one of the strongest European empires during the Middle Ages. The capital city was Constantinople.Black Death - A deadly disease that spread through much of Europe during the Middle Ages. It is estimated that it killed at least one third of all the people in Europe.Castle - A defensive fortification where a lord or king would live. The local people would flee to the castle if they were attacked.Charlemagne - King of the Franks and the first Holy Roman Emperor, Charlemagne united much of western Europe during his reign.Chivalry - The code by which knights pledged to live. It involved honor, being courageous, and protecting the weak.Coat of arms - A symbol used by knights on their shield, banner, and armor. It helped to distinguish one knight from another.Crusades - Religious wars between the Christians and Muslims for control of the Holy Land, especially Jerusalem.Feudal System - A system of government where the king allotted land to his lords and barons.
The lords and barons would then pledge their loyalty to the king and promise to protect his rule.Fief - An area of land given to a lord or baron by a king to rule.Franks - Germanic tribes who settled in the land that is today France. Guild - An association of craftsmen that focused on a specific trade or craft such as making shoes or weaving cloth.Journeyman - A position in a guild above the apprentice, a journeyman worked for a master craftsman and earned a wage.Keep - A large tower within a castle that was considered the last line of defense.Kievan Rus - An empire founded by Vikings in the city of Kiev. It was the forerunner of Russia.King - The top ruler in a monarchy.Knight - A warrior who rode a horse and wore heavy metal armor.
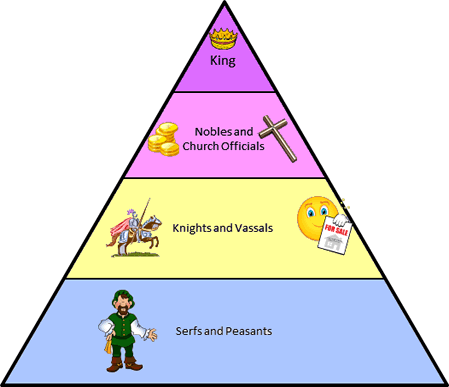
Feudal system definition, the political, military, and social system in the Middle Ages, based on the holding of lands in fief or fee and on the resulting relations between lord and vassal. Under the feudal system land was granted to people for service. It started at the top with the king granting his land to a baron for soldiers all the way down to a peasant getting land to grow crops. The Manor The center of life in the Middle Ages was the manor. The manor was run by the local lord.
Knights were rewarded with land and were required to protect the king when needed.Magna Carta - A document forced upon King John of England by his barons. It said that the king was not above the law and that the people had the right to a fair trial.Manor - The center of life during the Middle Ages, the manor was the local lord's house or castle.Moat - A ditch around a castle filled with water.Monastery - A religious area or group of buildings where monks lived. Monasteries were isolated from the rest of the world so the monks could focus on worshiping God. Also called an Abby.Master - The highest position in a guild, a master could own a shop and hire journeymen and apprentices.Page - A young boy that acts as a servant for a knight while training to become a knight someday.Reconquista - The wars where the Christian nations took back control of the Iberian Peninsula (Spain and Portugal) from the Muslim Moors.Serf - A peasant who worked the land for the local lord. The serf had few rights and was little better than a slave.Squire - A knight in training, the squire would take care of the knight's armor and weapons. He would also accompany the knight into battle.
A feudal system (also known as feudalism) is a type of social and political system in which landholders provide land to tenants in exchange for their loyalty and service.Feudalism prevailed in the Middle Ages in Europe and Japan and generally involved a lord (the landowner) allowing (tenants) to rent the land by providing services, especially military service. The parcel of land, called a, was typically worked by, laborers who had very few rights and were bound to the land itself.The term feudal system is often used in a much more general way in political rhetoric to indicate an outdated, exploitative system of government. This usage may or may not actually refer to relationships that don’t look anything like historical feudal systems. The feudal system developed in Europe when the decline of the Roman Empire led to a fragmentation of power, which in turn allowed wealthy landowners to strengthen their control over the people living on their land. But they didn’t call it a feudal system at the time. The term feudal system was introduced much later, in the 1700s, by scholars studying the complex legal and political relationships of the Middle Ages.The word feudalism may call to mind images of lowly peasants toiling for haughty nobles, but the relationships in such systems were more complex than that. At the top of the in the feudal system was a king, who traditionally owned all land and granted it directly to noblemen, known as lords, who held hereditary rights to it.
Their tenants, called vassals, swore loyalty to the lord and provided military service (yes, knights in shining armor). Working the land (doing the actual farming) at the very bottom of the hierarchy were peasants called serfs. Serfs were not free to work elsewhere or go wherever they pleased—if the land passed from one owner to another, the serfs were then required to work the land for that new owner.
And they were required to get the lord’s permission to do just about anything, including getting married or traveling off of the land.Feudalism wasn’t limited to medieval Europe. Darkest of days free download. Japan operated under a feudal system from the 1100s to the 1800s under powerful military leaders called, whose vassals, called, controlled armies of. At the bottom of the hierarchy were farmers and merchants.While such systems essentially no longer exist, the term feudal system is still often heard in political discourse as a negative term for unfair forms of government. This usage doesn’t usually refer to the actual structural complexities of feudalism, but rather is intended to draw a comparison based on how unequal and unjust such systems were.